
Quantum AI Ethics: Job Market Impact
Quantum AI is reshaping industries by combining artificial intelligence with quantum computing, offering immense computational power but introducing complex ethical challenges. Key takeaways include:
- Job Market Shift: Automation is impacting routine jobs like data entry and customer support, while creating demand for specialized roles in AI ethics, governance, and quantum technologies.
- Ethical Concerns: Risks include potential cybersecurity threats (e.g., breaking encryption), bias in AI systems, and widening economic disparities due to high costs and skill demands.
- Reskilling Needs: Workers must focus on acquiring technical, regulatory, and ethical skills to remain relevant, with opportunities in fields like AI oversight, quantum governance, and cybersecurity.
- Growth Trends: The quantum computing market is projected to grow from $866M in 2023 to $4.375B by 2028, with long-term expansion expected to reach $50B in the next decade.
The article emphasizes the importance of balancing innovation with ethical considerations and workforce preparation to address both opportunities and challenges in the Quantum AI era.
Chief in Tech S1E4 - 10x Human: AI, Quantum, and the Future of Work (Dr. Kristin M Gilkes,...
How Ethics Shape Quantum AI Development
Ethical considerations are now at the forefront of Quantum AI design and deployment. As the global quantum technology market heads toward an estimated value of $173 billion by 2040, developers and organizations are realizing that principles like transparency, accountability, and bias reduction must be baked into these systems from the very beginning. Without these guardrails, Quantum AI could amplify existing challenges in unforeseen ways.
To prevent such outcomes, researchers are working to establish shared ethical guidelines before Quantum AI sees widespread use. As highlighted in Nature Physics, "The time has come to consider appropriate guardrails to ensure quantum technology benefits humanity and the planet". A practical step in this direction includes the use of tools like "Responsible Research and Innovation (RRI) Prompts and Practice Cards", which help identify ethical risks during the development phase.
This focus on ethics is also reshaping how companies operate. Many now rely on cross-functional Quantum Task Forces that bring together HR, IT, and business units to ensure accountability across a variety of applications - from optimizing supply chains to making decisions in healthcare. By laying this ethical groundwork, organizations are better equipped to tackle one of the most pressing concerns: reducing bias in Quantum AI systems.
Reducing Bias in Quantum AI Systems
Bias in AI systems isn’t just a technical hurdle - it’s a serious legal and reputational risk. A 2025 case involving Workday and HiredScore AI underscored this when a federal judge ruled that AI tools used in hiring could be considered "agents" of the employer, making companies liable for discrimination based on race, age, or disability. This ruling makes it clear that employers can’t deflect responsibility onto AI systems.
To address these risks, practical solutions are emerging. For instance, research shows that having recruiters complete an Implicit Association Test (IAT) before using AI screening tools can increase the selection of non-stereotypical candidates by 13%. Interestingly, even when AI suggestions are seen as less than ideal, human decision-makers still follow AI recommendations 90% of the time.
Regulations are also stepping in. In New York City, mandatory bias audits for AI hiring tools are now in place, and with 93% of Fortune 500 CHROs incorporating AI into hiring processes, bias reduction has become a necessity. States like California and Colorado are preparing similar regulations for 2025–2026, requiring companies to take "reasonable care" in avoiding algorithmic discrimination.
While reducing bias is critical, it’s only part of the equation. Transparency and accountability are equally essential to ensure trust and fairness in these systems.
Building Transparent and Accountable Systems
Transparency is key to demystifying Quantum AI and separating genuine progress from exaggerated claims. To address this, organizations are rolling out tiered training programs. These range from basic awareness sessions for all employees to advanced, in-depth training for specialized quantum teams. The goal is to ensure that everyone involved understands both the potential and the limitations of the technology.
Accountability frameworks are also evolving to meet the unique challenges of Quantum AI. Companies are developing "Quantum Policy and Ethics Roadmaps" to guide executives as they evaluate partnerships and make ethical investment decisions. These frameworks raise critical questions: Who is responsible if a quantum-enhanced AI system makes a discriminatory decision? How can these systems be audited when they operate at speeds and scales beyond traditional oversight? The answers lie in combining technical safeguards with well-defined accountability structures.
Industries like finance and healthcare, where the stakes are especially high, are leading the charge. In finance, a biased quantum algorithm could reject loans for entire demographic groups in mere milliseconds. In healthcare, flawed quantum-enhanced diagnostic tools could result in systematic misdiagnoses. To mitigate these risks, these sectors are investing heavily in robust validation protocols and human-in-the-loop systems, ensuring that human judgment remains a critical part of the decision-making process. This ethical rigor not only enhances system reliability but also redefines roles in oversight and regulatory compliance, paving the way for a more responsible future.
Job Displacement Risks by Industry
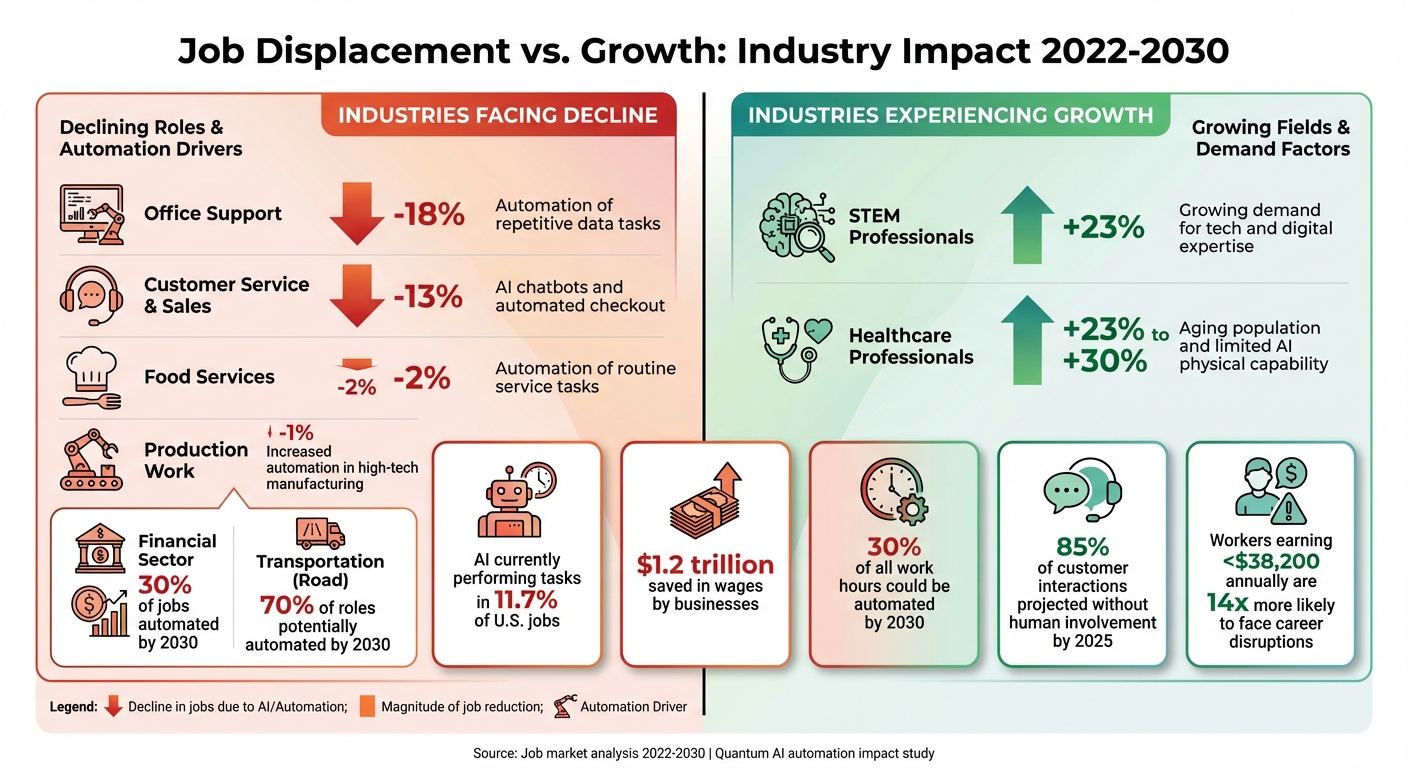
Quantum AI Job Market Impact by Industry 2022-2030
Quantum AI's influence on the job market is far from uniform. Understanding which sectors are most at risk can help workers and employers plan for the changes ahead.
Routine Tasks vs. Creative Work: Who's at Risk
Jobs that rely heavily on routine, repetitive tasks are the most vulnerable to automation, while roles requiring creativity or physical, hands-on work remain relatively secure. As Yoshua Bengio, Professor at Université de Montréal, explains:
"Cognitive jobs, the jobs that you can do behind a keyboard, will be the first casualties of automation. It's just a matter of time."
The data backs this up. Currently, AI is performing tasks in 11.7% of U.S. jobs, saving businesses an estimated $1.2 trillion in wages. By 2030, as much as 30% of all work hours could be automated. Positions like interpreters, translators, historians, sales representatives, writers, and customer service representatives - all of which involve processing information digitally - are among the most at risk. On the other hand, hands-on jobs such as dredge operators, water treatment plant operators, and floor sanders remain relatively safe from automation.
Income disparities further complicate the picture. Workers earning less than $38,200 annually are 14 times more likely to face career disruptions due to automation. This creates a troubling scenario where those with fewer resources face the greatest upheaval.
This divide between vulnerable and secure occupations sets the stage for a closer look at how specific industries are affected.
Industry-by-Industry Displacement Analysis
The impact of automation varies widely across industries, with some sectors facing steep declines while others experience growth.
Office support roles are expected to see an 18% decline by 2030, largely due to the automation of repetitive data entry and administrative tasks. Similarly, customer service and sales positions could shrink by 13%, as AI chatbots and automated checkout systems handle more routine interactions. By 2025, 85% of customer interactions are projected to occur without human involvement.
The financial sector is another area under significant pressure, with 30% of jobs potentially automated by 2030. In 2025, Salesforce CEO Marc Benioff highlighted this trend, revealing that the company had cut 4,000 customer support roles because AI was handling up to 50% of the workload. Benioff noted:
"I've reduced it [customer support] from 9,000 heads to about 5,000, because I need less heads."
Transportation jobs, particularly in road transport like truck driving, face an even steeper challenge, with 70% of roles potentially automated by 2030. Similarly, manufacturing jobs, especially in assembly lines and quality control, are being reshaped as AI-driven robots outperform humans in speed and accuracy.
| Industry/Occupational Category | Estimated Job Demand Change (2022-2030) | Primary Driver of Displacement |
|---|---|---|
| Office Support | -18% | Automation of repetitive data tasks |
| Customer Service & Sales | -13% | AI chatbots and automated checkout |
| Food Services | -2% | Automation of routine service tasks |
| Production Work | -1% | Increased automation in high-tech manufacturing |
| STEM Professionals | +23% | Growing demand for tech and digital expertise |
| Healthcare Professionals | +23% to +30% | Aging population and limited AI physical capability |
While industries like office support and transportation face significant automation risks, others, such as healthcare and STEM fields, are poised for growth. These sectors benefit from increasing demand for human expertise and physical presence, areas where AI still falls short. As Quantum AI continues to reshape the job market, the challenge for workers lies in determining where their current roles fit into this shifting landscape - and preparing for what’s next.
New Jobs in Quantum AI Ethics and Oversight
As automation reshapes job markets, Quantum AI is creating opportunities in ethical oversight and governance. A recent survey found that 77% of organizations are actively developing AI governance strategies, and 98.5% plan to hire oversight staff within the next year. This marks a notable shift in how companies approach technology and its ethical deployment.
Top In-Demand Quantum AI Ethics Positions
The rise of Quantum AI has sparked demand for new roles focused on ethics and governance. Mentions of "Responsible AI" in job postings grew from nearly nonexistent in 2019 to 0.9% by 2025. Similarly, job postings requiring quantum skills tripled between 2011 and mid-2024. These trends highlight the emergence of specialized positions.
AI Ethics Officers lead efforts to ensure ethical AI implementation, emphasizing bias reduction and corporate responsibility. They translate complex regulations - like the EU AI Act - into actionable policies. AI Governance Specialists focus on regulatory compliance and risk management, with the U.S. legal sector showing the highest share of Responsible AI mentions at 3.5% of AI-related postings, followed by banking and finance at 2.3%.
Fairness Engineers work to develop and test algorithms that promote transparency and eliminate bias. Red Teaming Specialists conduct adversarial testing to identify vulnerabilities in AI and quantum systems before they cause harm. The IAPP AI Governance Profession Report 2025 notes:
"AI governance skills will continue to evolve alongside the development of new types of AI technologies and policies. Certain skills, such as red teaming, will be increasingly necessary".
Quantum Governance Leads oversee the integration of quantum systems into business operations, requiring a mix of technical expertise and strategic insight. Jonathan Ruane, Senior Lecturer and Research Scientist at MIT Sloan, observes:
"We expect to see a proliferation of folks who are not researchers in quantum technology gain employment in the broader quantum market."
Although 34% of quantum technology roles require a PhD, ethics and oversight positions often value diverse backgrounds in law, policy, finance, and business.
Required Skills for Quantum AI Oversight Jobs
These roles demand a blend of technical expertise and ethical understanding. Professionals need strong foundations in quantum algorithms, coding, computer science, and statistical data analysis. Cybersecurity knowledge, especially in quantum-safe cryptography, is becoming essential as quantum computing challenges current encryption standards .
Equally critical are skills rooted in Responsible AI principles, including fairness, transparency, and accountability. Professionals must identify and mitigate risks like inaccuracies, cybersecurity threats, and intellectual property issues. Familiarity with regulatory frameworks - such as the EU AI Act, GDPR, and national security-related investment restrictions - is also vital .
These roles require interdisciplinary expertise, combining technical skills with an understanding of law, policy, and business strategy. Communication skills are increasingly important to help non-technical stakeholders grasp the implications of quantum technologies.
| Skill Category | Essential Competencies | Relevant Roles |
|---|---|---|
| Technical | Quantum algorithms, coding, data science, cybersecurity | Fairness Engineer, Quantum Software Developer |
| Ethical | Bias reduction, transparency, accountability, AI safety | AI Ethics Officer, Responsible AI Lead |
| Governance | Regulatory compliance (EU AI Act), national security, IP law | Quantum Governance Specialist, Compliance Officer |
| Business | Strategic communication, reputation management, market analysis | Product Manager, Quantum Business Developer |
For those interested in transitioning into these roles, targeted upskilling is crucial. Legal and policy professionals can benefit from training in quantum mechanics fundamentals and AI ethics, especially for roles in banking and legal sectors . Technical experts can expand their quantum computing knowledge with certifications in AI safety, governance frameworks, and international trade law . Interestingly, 30% of organizations not yet using AI are already working on AI governance, opening doors for professionals even before widespread adoption.
Compensation varies, with large tech firms offering the most competitive packages. Job seekers can leverage tools like JobLogr (https://joblogr.com) for AI-driven career support, including resume building, job tracking, and interview preparation.
As the demand for these roles grows, reskilling efforts will play a key role in meeting the evolving needs of the job market.
sbb-itb-6487feb
Reskilling for the Quantum AI Job Market
Between 2018 and 2023, quantum job postings skyrocketed by 450%. Despite this growth, there’s a significant talent gap: for every three job openings, there’s only one qualified candidate. By 2025, fewer than half of these positions are expected to be filled. As Quantum AI redefines industries and reshapes ethical norms, updating skills is no longer optional - it’s essential.
Gone are the days of single-career trajectories. Today’s workforce must embrace continuous skill development. Cybersecurity expert Marcio De Paula Wai puts it succinctly:
"Old model: 'I need a job that lasts 20 years.' New model: 'I need skills that remain relevant every 3 years.'"
This shift from job security to skill adaptability is critical across sectors like finance and pharmaceuticals. The growing skills gap highlights the urgent need for effective reskilling initiatives.
Effective Reskilling Programs
The most successful reskilling efforts follow a tiered approach, building expertise step by step. One proven strategy involves a four-level training framework:
- Level 1 (Awareness): A brief 2–4 hour session introducing key terms and the broader impact of quantum technologies.
- Level 2 (Literacy): A 2–3 day program tailored for business professionals, focusing on identifying quantum use cases and understanding how quantum and classical systems integrate.
- Level 3 (Proficiency): A 1–2 week hands-on workshop for technical teams, offering experience with tools like Qiskit, Cirq, and Q#.
- Level 4 (Expertise): Continuous advanced training in areas such as algorithms, error correction, and hardware optimization.
For those already in tech, reskilling is achievable within months. Software engineers and AI developers can master quantum tools in about six months, while professionals in adjacent fields - like statistics, computer science, or chemistry - can train as "quantum translators" in three to six months. These translators play a vital role by connecting technical quantum capabilities with practical business applications.
Some companies are already making bold moves. In 2025, BT Group announced plans to cut 10,000 jobs due to AI-driven efficiencies but pledged to retrain 5,000 employees for specialized roles in cybersecurity and network resilience. Similarly, IBM paused hiring for around 7,800 administrative positions while expanding its quantum research and cybersecurity teams to meet post-quantum cryptography goals by 2030. Mastercard also rolled out a generative AI-powered digital assistant in late 2025, prompting a large-scale internal upskilling initiative focused on AI governance.
Here’s a quick snapshot of the training framework:
| Training Level | Target Audience | Duration | Key Focus |
|---|---|---|---|
| Level 1: Awareness | All Employees | 2–4 Hours | Basic terminology, industry impact, separating hype from reality |
| Level 2: Literacy | Business Professionals | 2–3 Days | Identifying use cases, understanding quantum–classical integration |
| Level 3: Proficiency | Technical Teams | 1–2 Weeks | Hands-on programming and experience with tools like Qiskit, Cirq, Q# |
| Level 4: Expertise | Quantum Specialists | Ongoing | Advanced algorithms, error correction, hardware optimization |
Reskilling doesn’t have to break the bank. Many public libraries in the U.S. provide free access to platforms like LinkedIn Learning, Udemy, and O’Reilly with just a library card. Setting quarterly goals - like learning one new digital skill every three months - can help workers stay on track. Non-technical professionals can focus on "quantum-safe" skills such as risk analysis, compliance, and privacy law to prepare for the quantum shift.
Training for Human-AI Collaboration
Adapting to the quantum AI era isn’t just about technical know-how; it’s also about mastering human-AI collaboration. By Spring 2025, nearly half of all workers (47%) reported using AI tools at least once a month, up from 34% in 2024. This surge in adoption underscores the need for training programs that emphasize how humans and AI can work together effectively. Workers must learn to harness AI’s computational power while applying critical thinking, ethical judgment, and industry expertise.
The future of work will feature "retooled" roles - jobs that retain their traditional titles but evolve with AI and quantum integration. For instance, financial analysts will still evaluate portfolios but may use quantum algorithms for risk modeling. Similarly, supply chain managers could leverage quantum computing to optimize complex routing problems. These roles require training that combines technical literacy with strategic problem-solving and emotional intelligence.
Jaime Teevan, Microsoft’s Chief Scientist, highlights this need:
"We have to intentionally design AI to think about collaboration and not just individual output, and organizational leaders need to be thinking about how they're restructuring their organizations in order to support that collaborative work."
To encourage collaboration, reskilling programs should include team-based exercises, cross-functional projects, and regular "knowledge hours" where quantum teams share progress with business and IT units. Organizations are also turning to Quantum-as-a-Service (QaaS) platforms, which allow non-experts to experiment with quantum tools at low cost, making hands-on learning more accessible.
For job seekers navigating these changes, platforms like JobLogr provide AI-driven tools for resume building, interview prep, and job tracking - helping candidates showcase their reskilling efforts in an increasingly competitive market.
Matt Garman, CEO of Amazon Web Services, sums it up well:
"The technology is moving at an incredible rate… it's hard for everyone to keep up."
With structured training programs, accessible resources, and a focus on continuous learning, workers can stay ahead in this rapidly evolving quantum AI landscape. These strategies not only prepare individuals for new opportunities but also align with broader goals of building future-ready careers.
Job Market Forecasts and Ethical Solutions
The rise of quantum AI is reshaping industries in profound ways, requiring a careful balance between technological progress and workforce stability.
Quantum AI Job Market Changes: 2025-2045
Recent trends show a growing divide in the workforce based on age. Workers aged 22–25 in high AI-exposure roles have seen their numbers decline by 6% since late 2022, while those aged 30 and older have experienced increases ranging from 6% to 13%. The youngest software developers have been hit the hardest, with their employment levels dropping 20% below their late 2022 peak by mid-2025.
This disparity highlights how AI and quantum tools are transforming industries. While experienced professionals are seeing their roles enhanced by these technologies, entry-level tasks are increasingly being automated. Industry leaders report significant cuts in entry-level positions, particularly in customer support and software development.
Looking ahead, the job market will likely evolve in phases:
- 2025 to 2030: Early-career roles in software development and customer support will continue to decline, but there will be growth in jobs tied to data center construction and AI training.
- 2030 to 2035: As quantum AI reaches a projected $50 billion market size, automation will expand across cognitive desk jobs, with finance and cryptography sectors facing the most disruption.
- 2035 to 2045: AI-driven robotics will begin to impact physical trade jobs, though these roles are expected to remain relatively stable in the short term.
Despite concerns about job losses, the data paints a more complex picture. In 2024, AI growth added 119,900 direct jobs in the U.S., while only 12,700 jobs - just 0.1% of all layoffs - were attributed to AI. Additionally, the construction of large-scale data centers for AI and quantum infrastructure has a ripple effect, creating 3.5 local jobs for every one job within the facility.
These shifts underscore the need for proactive policies to support workers while fostering innovation.
Policy Recommendations for Ethical AI Implementation
To navigate these changes, policymakers must strike a careful balance. Effective strategies should encourage innovation while addressing workforce challenges. Overly restrictive regulations could stifle economic growth, so a "wait-and-watch" approach - observing occupational trends before imposing limits - is essential.
Rather than focusing on preserving specific roles, the emphasis should be on equipping workers with skills that thrive in an AI-driven world. Early-career professionals, in particular, need access to targeted reskilling programs that prepare them for roles enhanced by AI rather than replaced by it. High-complexity skills that complement AI are key to ensuring long-term employability.
Businesses also have a role to play. Conducting multi-stakeholder audits can help organizations assess the ethical implications of AI systems. These audits should involve input from employees, customers, and regulators, fostering transparency and accountability. Collaboration among technologists, ethicists, and policymakers is crucial to ensure quantum AI aligns with societal priorities.
In October 2025, Beth Galetti, Senior Vice President at Amazon, highlighted the scale of this transformation when the company announced the elimination of 14,000 corporate roles:
"This generation of AI is the most transformative technology we've seen since the Internet... we're convinced that we need to be organized more leanly".
The solution lies in what experts call "ethical agility" - the ability to adapt policies as quantum AI evolves. Regulations must be tailored to specific contexts, balancing innovation with job security and other societal goals. For job seekers, platforms like JobLogr offer AI-driven tools to craft resumes, prepare for interviews, and track applications, helping them stay competitive in this shifting landscape.
The quantum AI job market is a complex mix of job creation and displacement, with impacts varying across age groups, industries, and skill levels. Success will depend on a combination of forward-thinking policies, continuous reskilling, and ethical frameworks that place human well-being at the forefront of technological progress.
Conclusion
Quantum AI is reshaping the job market in profound ways. While there are concerns, such as projected layoffs of 55,000 in 2025, there's also a silver lining with the creation of 119,900 new roles anticipated in 2024. The real challenge lies in implementing these advancements ethically - protecting privacy, promoting inclusivity, and respecting individual autonomy .
As entry-level positions shrink and experienced professionals gain from AI-driven tools, it's becoming increasingly important to focus on human-centric skills like empathy, creative problem-solving, and original thinking. With the quantum technology sector poised for substantial growth, now is the perfect time to invest in quantum literacy and develop the ability to bridge technical know-how with business needs.
Platforms such as JobLogr are stepping in to help individuals adapt. These AI-powered tools streamline resume customization, interview preparation, and job application tracking, making it easier to target emerging roles in quantum AI ethics. Beyond personal empowerment, these tools are paving the way for a workforce that's better prepared for the changes ahead. Ongoing learning will remain a cornerstone of success.
Organizations that embrace reskilling and prioritize human-AI collaboration will thrive in this evolving landscape. Those that delay will risk falling behind. The job market isn't disappearing - it’s transforming, rewarding those who combine technical expertise with ethical insight and the ability to adapt to new challenges.
FAQs
How might Quantum AI change job roles in customer service and data entry?
Quantum AI merges the lightning-fast processing of quantum computing with the advanced decision-making capabilities of artificial intelligence. This powerful combination is set to transform roles like customer service and data entry. By automating repetitive tasks - such as inputting data or managing scripted customer interactions - businesses can tackle larger workloads and address more complex queries without depending as heavily on human workers.
For those currently in these roles, this shift underscores the growing need for reskilling. Moving into fields like AI oversight, prompt engineering, or positions that demand empathy and creative problem-solving will be crucial. Tools like JobLogr can play a pivotal role in this transition by helping individuals explore new career paths, refine their resumes to highlight emerging skills, and discover opportunities in roles that work alongside AI systems. Adapting to these changes will be key to thriving in a rapidly evolving job landscape.
What ethical guidelines are being developed to reduce bias in Quantum AI systems?
Ethical guidelines for addressing bias in Quantum AI are steadily developing through collaborative efforts that merge traditional AI ethics with the distinct aspects of quantum technologies. The focus remains on ensuring fairness, transparency, and accountability, so these advanced tools don’t end up amplifying existing inequalities.
Take, for instance, the "10 Principles for Responsible Quantum Innovation." These principles advocate for practices like using diverse training data, conducting bias impact assessments, and maintaining ongoing model monitoring. Similarly, the U.S. National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) is adapting its AI Risk Management Framework to include quantum AI. Their efforts center on minimizing bias, enhancing explainability, and thoroughly documenting how model decisions are made.
The emphasis here is clear: ethical safeguards must be integrated early in the development process. By involving multidisciplinary teams to guide and oversee these measures, the aim is to ensure that Quantum AI not only pushes technological boundaries but also upholds equity and fairness.
What skills do you need to pursue a career in Quantum AI ethics and oversight?
To pursue a career in Quantum AI ethics and oversight, you'll need a blend of technical expertise, ethical understanding, and practical abilities. Employers are particularly interested in candidates who grasp the fundamentals of quantum computing, the role of AI in decision-making, and the ethical dilemmas these technologies can present. Familiarity with quantum programming platforms like Qiskit or Cirq, along with experience in AI model auditing and bias detection, can set you apart.
Beyond technical skills, having a solid foundation in regulatory knowledge is key. This means staying updated on new standards, crafting compliance frameworks, and evaluating the societal implications of AI-quantum technologies. Additionally, effective communication and leadership abilities are vital for working with diverse teams and simplifying complex ideas into actionable plans for stakeholders.
Since this field is still developing, professionals should embrace interdisciplinary collaboration and remain flexible. Tools like JobLogr can be a valuable resource, helping you pinpoint the skills you need, refine your resume, and prepare for interviews to succeed in this rapidly evolving industry.