
Green Job Trends: Renewable Energy Insights
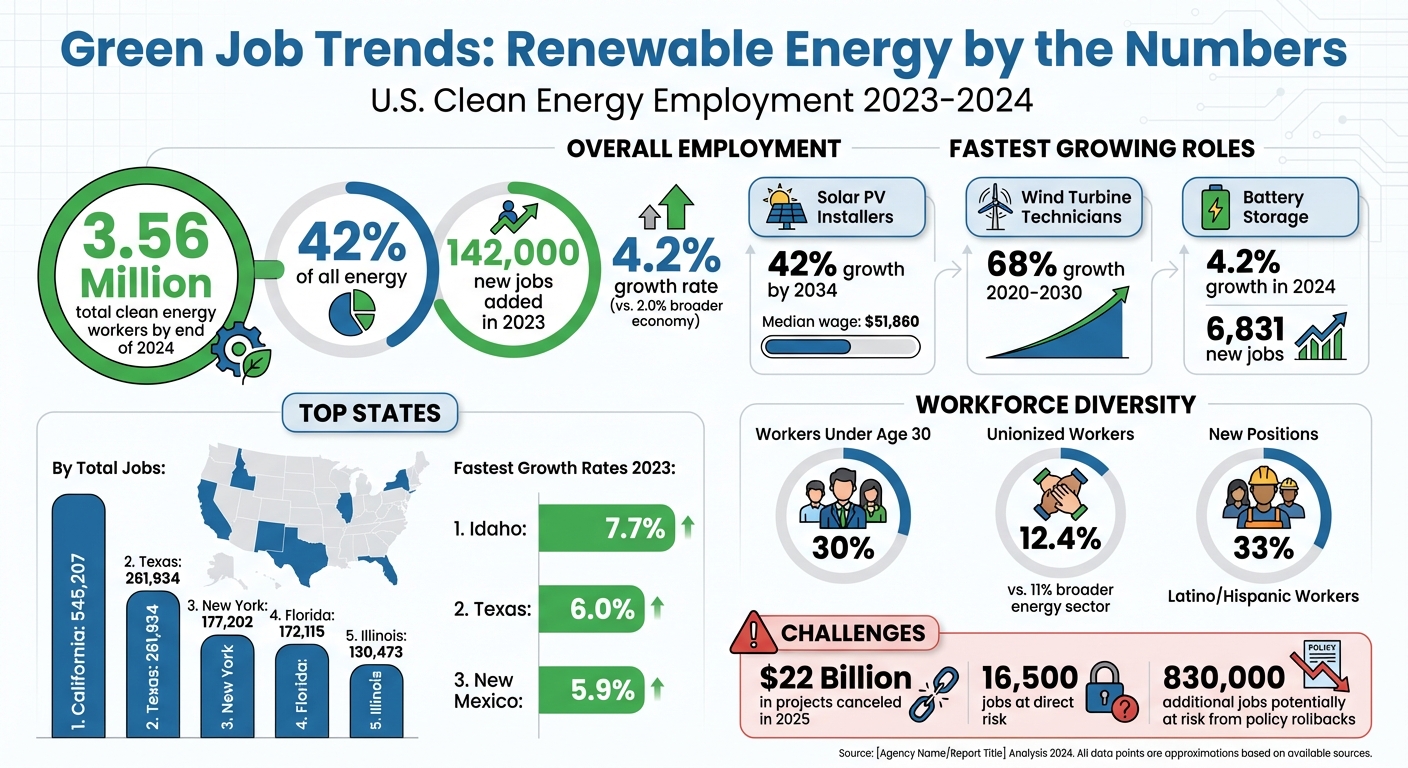
The U.S. renewable energy sector is growing faster than most industries, adding 142,000 new jobs in 2023 alone - a 4.2% increase compared to the broader economy's 2.0% growth. By the end of 2024, the sector employed 3.56 million workers, accounting for 42% of all energy jobs. Solar and wind energy lead the charge, with solar jobs growing by 5.3% and wind by 4.5% in 2023.
Key Takeaways:
- Unionization: 12.4% of clean energy jobs were unionized in 2023, higher than the broader energy sector's 11%.
- Diversity: Nearly 30% of workers were under 30, and Latino/Hispanic workers filled one-third of new positions.
- Top Jobs: Solar PV installers and wind turbine technicians are among the fastest-growing roles, with solar PV installer jobs expected to grow 42% by 2034.
- Regional Leaders: California, Texas, and New York dominate clean energy employment, while states like Idaho and New Mexico show the fastest growth.
Despite rapid expansion, challenges like policy uncertainty and technical hurdles could slow progress. Over $22 billion in projects were canceled in 2025, putting thousands of jobs at risk. However, growth areas like battery storage and grid modernization remain promising for job seekers.
For anyone looking to enter this field, focusing on fast-growing roles and leveraging union apprenticeships or technical training can open doors to opportunities in this expanding industry.
U.S. Renewable Energy Job Growth Statistics 2023-2024
Job Growth Rates in Renewable Energy
Clean Energy Employment Numbers
The renewable energy sector has seen impressive job growth over the past five years. According to recent data, clean energy companies added over 520,000 jobs between 2020 and 2025, marking a 17% increase - outpacing traditional energy industries. By the close of 2024, clean energy employment in the U.S. reached 3.56 million workers.
In 2024 alone, clean energy jobs grew by 2.8%, adding roughly 95,700 positions. Renewable energy generation saw a 3.9% rise, creating 9,338 new jobs and totaling 569,309 workers. Meanwhile, storage and grid modernization roles expanded by 4.2%, contributing 6,831 new jobs for a total of 168,042. Notably, 82% of all new energy sector jobs that year were in clean energy. Since 2020, clean energy companies have added jobs at a pace 60% faster than the broader economy.
How Renewable Energy Compares to Other Sectors
The growth in clean energy jobs stands in stark contrast to slower trends in other industries. While clean energy jobs grew by 2.8% in 2024, the overall U.S. workforce expanded by just 0.8% - making clean energy’s growth more than three times faster. Between 2021 and 2024, clean energy employment rose by 12%, compared to an 8% increase for the total U.S. job market.
When compared to traditional energy sectors, the difference is even more striking. Clean energy electricity generation jobs grew by 11% between 2021 and 2024, while jobs in traditional energy sources like natural gas, coal, and oil increased by just 7%. Although fossil fuel extraction jobs experienced a temporary 18% surge during that time, they are expected to decline by 6% over the next decade as the shift to clean energy accelerates.
"These jobs are now a vital anchor of America's energy workforce. The strength of the U.S. job market and the future of our energy economy are now inseparable from the growth of clean energy."
- Michael Timberlake, Director of Research and Publications, E2
Top Jobs in Renewable Energy
Solar Photovoltaic Installers
Solar photovoltaic (PV) installers are responsible for designing system layouts, assembling support structures, installing panels, and connecting them to the electrical grid. According to the Bureau of Labor Statistics, this field is expected to grow by 42% from 2024 to 2034, translating to about 4,100 job openings annually. Employment in this role is projected to rise from 28,600 to 40,600 positions during that period.
A high school diploma is typically required, along with up to one year of on-the-job training. The median annual wage for solar PV installers was $51,860 in May 2024. The job can be physically demanding, involving work at heights, lifting up to 60 pounds, and applying basic math skills. Nearly half (44%) of these professionals work for electrical and wiring installation contractors, while 14% are employed directly by utility companies.
Solar Manufacturing and Supply Chain Positions
The renewable energy sector is also seeing growth in manufacturing and supply chain roles, driven by federal investments. For example, U.S. solar module production capacity surged from 8 GW before the Inflation Reduction Act to 42 GW by 2024. This expansion has created a variety of jobs in production, quality control, logistics, and management. Around 35% of workers in this sector are directly involved in manufacturing operations.
The adoption of digital tools, remote monitoring systems, and AI technologies is further improving efficiency and increasing demand for workers with technical skills.
Construction and Professional Services Roles
In addition to installation and manufacturing, renewable energy projects heavily rely on traditional construction trades. Electricians handle grid connections for solar systems, roofers prepare surfaces for panel installation, and general laborers manage site preparation and equipment transportation. Workers with experience in these trades can often transition into solar-specific roles with minimal additional training.
For those with experience, there are opportunities to advance into roles like project supervisor, project manager, or specialized sales positions. Industry data shows that 33% of the solar workforce focuses on installation and repair, while 20% hold management or professional roles, and 15% work in sales. These construction and professional service jobs form the backbone of renewable energy projects, ensuring that plans become operational power systems.
Where Renewable Energy Jobs Are Growing
States with the Most Renewable Energy Jobs
California stands at the forefront of the clean energy job market in the U.S., boasting 545,207 positions as of 2023. This leadership stems from decades of investments in solar infrastructure and forward-thinking environmental policies. However, the state's residential solar market hit a snag in 2024 when NEM 3.0 slashed compensation for exported power by about 75%.
Trailing California, Texas secures second place with 261,934 clean energy jobs. The state benefits from massive solar and wind projects that cater to its increasing electricity demands. New York ranks third with 177,202 positions, followed by Florida with 172,115 jobs, and Illinois rounding out the top five at 130,473 jobs. Meanwhile, Nevada has held the top spot for solar jobs per capita for four straight years, proving that smaller states can punch above their weight when supported by favorable policies.
States with the Fastest Job Growth
While some states lead in sheer numbers, others are making waves with rapid job growth. Idaho posted the fastest clean energy job growth rate in 2023, climbing 7.7%. Texas and New Mexico followed closely, with growth rates of 6.0% and 5.9%, respectively. This surge is largely driven by utility-scale solar and battery storage projects in the Southwest, where abundant land and solar resources create ideal conditions for large-scale installations.
In fact, clean energy jobs grew across all 50 states and the District of Columbia in 2023, marking a nationwide growth rate of 4.2% - more than double the U.S. economy's overall growth rate of 2.0%.
sbb-itb-6487feb
What to Expect in the Coming Years
Growth Forecasts by Energy Type
The renewable energy sector is poised for steady expansion, although growth rates differ significantly depending on the occupation. For instance, wind turbine service technicians are projected to see a 68% increase in employment between 2020 and 2030, translating to about 4,700 new jobs. Similarly, solar photovoltaic installers are expected to grow by 52% during the same period, adding approximately 6,100 positions. In fact, the Bureau of Labor Statistics lists these two roles among the fastest-growing occupations in the United States.
That said, the overall job growth in renewables is still relatively modest when compared to larger economic sectors. Solar energy growth primarily revolves around new installations, while wind energy jobs are increasingly focused on maintenance. In 2024, clean energy jobs expanded at a rate 3.5 times faster than the broader U.S. economy, although the growth rate slowed from 4.2% in 2023 to 2.8%.
Battery storage is another area showing strong momentum. Between 2010 and 2018, U.S. storage capacity jumped from 59 megawatts to 869 megawatts, while storage costs fell by 61% from 2015 to 2017. In 2024 alone, the storage and grid sector added 6,831 jobs, reflecting a 4.2% growth rate.
These trends highlight the sector's potential, but they also underscore the need to address challenges that could impede progress.
Potential Obstacles to Job Growth
Despite encouraging growth projections, the renewable energy sector faces several hurdles. One major issue is policy uncertainty, which continues to threaten job creation in 2024 and into early 2025. Since January 2025, over $22 billion worth of projects have been canceled due to shifting policies, putting 16,500 jobs directly at risk. Additionally, rollbacks enacted in July 2025 could jeopardize another 830,000 positions.
"Now, clean energy job growth is at serious risk – and with it, our overall economy"
- Bob Keefe, Executive Director of E2
Technical challenges add another layer of complexity. Renewable energy sources like wind and solar are dependent on weather conditions, leading to inconsistent production. To address this, advancements in large-scale battery storage are critical for bridging production gaps. Furthermore, the expiration of renewable energy tax credits could significantly impact future costs. For example, the current cost of a typical 6-kilowatt residential solar installation is approximately $17,760 before tax credits and $13,142 after credits.
These challenges underscore the need for sustained policy support and technological innovation to ensure the sector's continued growth and stability.
Conclusion
Main Findings
The renewable energy sector has become a major force in shaping the U.S. job market. By the end of 2024, it employed 3.56 million workers, making up 42% of all energy jobs. Clean energy alone accounted for 82% of new positions, growing at a rate of 2.8% - more than three times faster than the overall U.S. workforce.
Energy efficiency continues to be the largest employer in this space, with 2,381,744 workers. Meanwhile, renewable generation, especially solar and wind, is experiencing the most rapid growth at 3.9%. Occupations like wind turbine service technicians and solar photovoltaic installers rank among the fastest-growing jobs in the country. The U.S. South has emerged as a hotspot for clean energy employment, now supporting over 1 million workers.
Still, the sector faces challenges. In 2025 and 2026, growth is under threat, with over $22 billion in canceled projects since January 2025 jeopardizing 16,500 jobs. Additionally, legislation passed in July 2025 could put another 830,000 positions at risk.
Tips for Job Seekers
Despite these challenges, job seekers can tap into the opportunities this sector offers by refining their skills and leveraging digital tools. Renewable energy remains a promising career path, especially in states like California, Texas, and Florida, or emerging markets such as Idaho, New Mexico, and Oklahoma. Focus on fast-growing roles in energy efficiency, solar installation, and battery storage, as these areas continue to expand even during economic challenges.
Consider union apprenticeships and specialized training programs. Unionization in clean energy reached 12.4% in 2023, surpassing the average for the broader energy sector. Employers note that partnerships with unions help them secure skilled labor and foster diversity within their teams.
To streamline your job search, use AI-driven tools like JobLogr (https://joblogr.com). These tools can automate searches, customize resumes for renewable energy roles, and track applications, giving you a competitive edge. As automation and new technologies make the sector more labor-efficient, staying ahead with digital tools can help you secure positions more quickly.
An Explosion of renewable energy projects is creating Thousands of NEW Jobs
FAQs
What challenges are impacting job growth in the renewable energy sector?
The renewable energy sector is buzzing with potential, but it’s grappling with some tough challenges that could slow its progress. One of the most pressing issues is the high job vacancy rate - hovering around 13.1%. That’s much higher than in other trade sectors and points directly to a growing skills gap. Simply put, there aren’t enough qualified workers to meet the demand.
Another hurdle is workforce retention. Factors like uncompetitive salaries, high turnover rates, and fierce global competition for skilled workers are making it tough to keep talent in the industry. On top of that, there’s an urgent need to build a more diverse and inclusive workforce to align with the ambitious goals set for renewable energy expansion.
Even though the demand for renewable energy is climbing, labor market inefficiencies and high entry barriers are creating bottlenecks in employment growth. Overcoming these obstacles will be critical to keeping the sector on track and meeting long-term decarbonization goals.
What steps can job seekers take to build a career in renewable energy?
Job seekers looking to break into the renewable energy industry can take a few practical steps to set themselves apart. Start by building the right skills and earning certifications in areas like solar, wind, energy efficiency, and grid management. Since many roles in this field require technical know-how, completing specialized training programs or obtaining certifications can make a big difference in your job prospects.
Pay attention to where the jobs are. States like Texas, California, and Michigan are currently leading the way in renewable energy employment. Staying on top of industry trends and policy updates can also help you spot opportunities as they emerge. Tools like JobLogr can simplify your search by providing AI-driven features for creating resumes, finding job matches, and preparing for interviews - making it easier to align your skills with what employers need.
Don’t underestimate the power of networking. Connecting with professionals, pursuing internships or apprenticeships, and gaining hands-on experience can give you an edge in this fast-growing field.
Which U.S. states have the most renewable energy job opportunities?
California, Texas, and Florida are at the forefront when it comes to job opportunities in renewable energy. Their robust solar industries and expanding clean energy initiatives make these states hotspots for careers in this sector. From installing solar panels to maintaining wind turbines, the variety of roles reflects their dedication to building out renewable energy infrastructure.
Although renewable energy jobs are spread across all 50 states, California stands out as a leader in solar-related employment. Its abundant sunshine and progressive energy policies have positioned it at the top. Not far behind, Texas and Florida are making their mark with large-scale renewable projects and an increasing demand for clean energy solutions.